Engraving Advice
All Emergency ID is engraved in clearly visible BLACK LASER text.
(black print was introduced on 1st July 2021 – when we invested in a state of the art high tech new engraving machine).
Engraving advice
Capitalise your SURNAME, so it is clear which is your surname, emergency services often do this to differentiate between first and surnames. Eg. Garry GRAHAM.
Feel free to use clear abbreviations eg T2 Diabetic or T2 Diabetes, instead of the full word of Type 2 Diabetic.
NO Morphine with NO capitalised to make it very clear they can’t have morphine, as opposed to just Morphine – as this may mean they are taking morphine.
Or you could word it as ALLERGY to Morphine. ANAPHYLAXIS to Morphine. Or even say how Morphine affects you ie Morphine = Skin Rash.
All items are custom engraved to suit the wearer’s needs, FREE of charge. We recommend you have engraved your most URGENT information as a 1st priority. Keep engraving short, clear and simple as a great IMMEDIATE & instant reference.
How much can be engraved on each item depends on your chosen style – some styles have more space to engrave than others, engraving spaces available are listed on each style.
I.C.E – In Case of Emergency
We recommend you have engraved an I.C.E. (In Case of Emergency) phone number on the back of your item. IE who you want to be called in an emergency. If you can fit the relationship to you into the ICE we recommend you do e.g ICE Sister 03 6381 1440. Their relationship with you is more relevant than their name.
Abbreviations
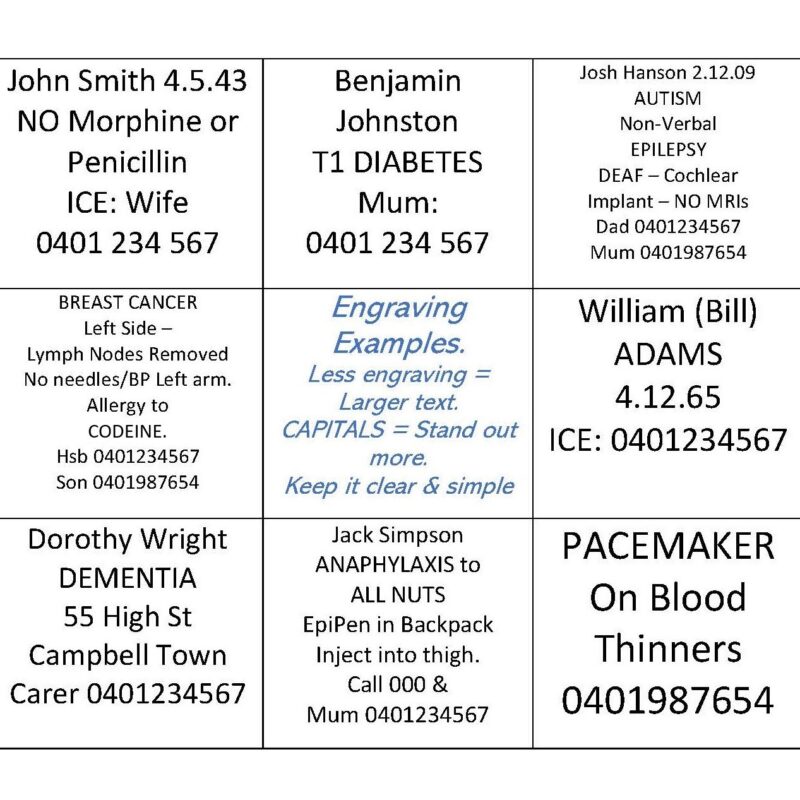
We can engrave full wording or medical abbreviations can also be used. See guides below. The less characters used, the larger we can engrave.
We also recommend that you were or carry more than 1 Emergency ID eg Emergency ID Photo Card, Emergency ID Medical Pouch, Emergency ID Write on card etc.
MEDICAL ABBREVIATIONS commonly used in Australia:
Please also consult your GP, specialist or medical professional and do your own research.
A
AAA abdominal aortic aneurysm
A&E accident and emergency
abdo abdomen/abdominal
ABG arterial blood gas
ac before meals
ACLS advanced care life support
ACS acute coronary syndrome
AED automatic external defibrillator
AF, A/F atrial fibrillation/atrial flutter
AFlut atrial flutter
AICD automated implantable cardioverter defibrillator
ALS advanced life support
AMI acute myocardial infarction
angio angiogram
ART arterial line (used for invasive pressure monitoring)
ATLS advanced trauma life support
AV atrioventricular
AVR aortic valve replacement
B
BGL blood glucose level
BLS basic life supoort
BP blood pressure
C
Ca cancer/calcium
CABG coronary artery bypass graft
CAD coronary artery disease
Card cardiac
cap capsule
CCB calcium channel blocker
CCF congestive cardiac failure
CCU coronary care unit
CF cystic fibrosis
CHF congestive heart failure
cm centimetre
CNS central nervous system
COAD chronic obstructive airway disease
CO carbon monoxide
CO2 carbon dioxide
COPD chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
CPAP continuous positive airways pressure
CPR cardiopulmonary resuscitation
CSF cerebrospinal fluid
CT computerised tomography
CVA cerebrovascular accident
CVL central venous line
CWMS colour warmth movement sensation
CXR chest x-ray
D
DCI decompression illness
DIC disseminated intravascular coagulation
DKA diabetic ketoacidosis
DM diabetes mellitus
DOB date of birth
Dr doctor
DVT deep vein thrombosis
E
eARF electronic ambulance report form
ECG electrocardiogram
ED emergency department
EEG electroencephalograph
EMD electromechanical dissociation
Emerg emergency department
ENT ear, nose and throat
ERYC erythromycin
ETT endotracheal tube
F
FAST focused abdominal sonography for trauma
FBC full blood count
FiO2 fractional inspired oxygen concentration
FR first responder
G
g gram(s)
GA general anaesthesia
GABA gamma amino butyric acid
GI gastrointestinal
GIT gastrointestinal tract
GORD gastro-oesophageal reflux disorder
GP general practioner
GU gastric ulcer
H
Hb haemoglobin
HI head injury
HIV human immunodeficiency virus
hrs hours
Hx history
I
ID band patient identification band/bracelet
IBS irritable bowel syndrome
IDC indwelling catheter
IDDM insulin dependent diabetes mellitus
IHD ischaemic heart disease
IM intramuscular
IMI intramuscular injection
IO intraosseous
ICC intercostal catheter
ICD implantable cardioverter defibrillator
ICP intracranial pressure
ICU intensive care unit
INH inhalation
inj injection
IV intravenous
IV inf intravenous infusion
IVABs intravenous antibiotics
IVI intravenous injection
IV Morph intravenous morphine
J
JVP jugular venous pressure
K
KCI potassium chloride
kg kilogram
Ko’d knocked out
KSAR known severe adverse reactions
KVO keep vein open
L
L litre
LA local anaesthetic
LAD left anterior descending (coronary artery)
lat lateral
LBBB left bundle branch block
LFT liver function test
LMA laryngeal mask airway
L/min litres per min
LMA laryngeal mask airway
LOC loss of consciousness
LVF left ventricular failure
M
MAOIs monoamine oxidase inhibitors
MAP mean arterial pressure
Max maximum
mcg microgram
mg milligram
MI myocardial infarction
mL millimetre(s)
mmHg millimetres of mercury
mmol millimole
MO medical officer (doctor)
MS multiple sclerosis
MVA motor vehicle accident
MVR mitral valve replacement
N
n/a not applicable
NAD nil abnormality detected
NAS intranasal
NC nasal cannulae
NEB nebulised
NFR not for resuscitation
NG/NGT nasogastric tube
NMDA N-Methyl D-Aspartate
NOF neck of femur
NOK next of kin
NSAIDs non steroidal anti inflammatory drugs
NSTEMI non-ST elevation myocardial infarct
O
Obs observations / vital signs
OE on examination
OPD outpatient’s department
OT occupational therapy
O2 oxygen
P
P pulse
PaCO2 partial pressure of carbon dioxide (arterial)
PaO2 partial pressure of oxygen (arterial)
PAC premature atrial contraction
PCI percutaneous coronary intervention (coronary angioplasty)
PE pulmonary embolism
PEA pulseless electrical activity
PEF peak expiratory flow
Physio physiotherapist
PID pelvic inflammatory disease
PJC premature junctional contraction
PMHx past medical history
PO Per oral
post-op post-operative
PPE personal protective equipment
PPH post-partum haemorrhage
p.r per rectum
prn when required
Pt patient
PV per vaginal
PVD peripheral vascular disease
PVC premature ventricular contraction
Q
R
RBBB right bundle branch block
RLQ right lower quadrant
ROSC return of spontaneous circulation
RSI rapid sequence induction
RUQ right upper quadrant
RV right ventricle
RVF right ventricular failure
S
SaO2 oxygen saturation
SB sinus bradycardia
sc subcutaneous
SFM simple face mask
sl sublingual
SNRI serotonin and noradrenaline re-uptake inhibitor
SOB shortness of breath
SR sinus rhythm
SSRI selective serotonin re-uptake inhibitor
ST sinus tachycardia
STEMI ST elevation myocardial infarction
SUBCUT subcutaneous
SUBLING sublingual
SVT supraventricular tachycardia
T
TCA tricyclic antidepressant
TCP transcutaneous pacing
THR total hip replacement
TIA transient ischaemic attack
TKR total knee replacement
TNK tenecteplase
Tx transplant
U
U/A urinalysis
UDB urinary drainage bag
URTI upper respiratory tract infection
UTI urinary tract infection
V
V/Q ventilation perfusion (lung scan)
VEB ventricular ectopic beat
VF ventricular fibrillation
VT ventricular tachycardia
W
WBC white blood cells
WNL within normal limits
Y
y/o year old
Miscellaneous
# fracture
1/60 one minute
1/24 one hour
1/7 one day
1/52 one week
1/12 one month
< less than
> greater than
≤ less than or equal to
≥ greater than or equal to
CAN BE PRINTED THROUGH THIS LINK: Australian Medical Abbreviations
To check medical abbreviations please consult a health professional or here are some example sites:
http://remotehealthatlas.nt.gov.au/acronyms_&_abbreviations_list.pdf
QAS-medical-Abbreviations.pdf (australianparamedicalcollege.com.au)
http://nursing.flinders.edu.au/students/studyaids/clinicalcommunication/…
We are PROUD of our products, outstanding reputation and award-winning customer service. We even encourage you to compare us to our competitors, MedicAlert and Universal Medical ID, by viewing the comparison table on our home page. We thank you for supporting a 100% Founded, Owned & Operated AUSTRALIAN business that sends Emergency ID WORLDWIDE!




